What are the advantages of ratio pyrometers vs single-wavelength pyrometers for steel manufacturing applications?
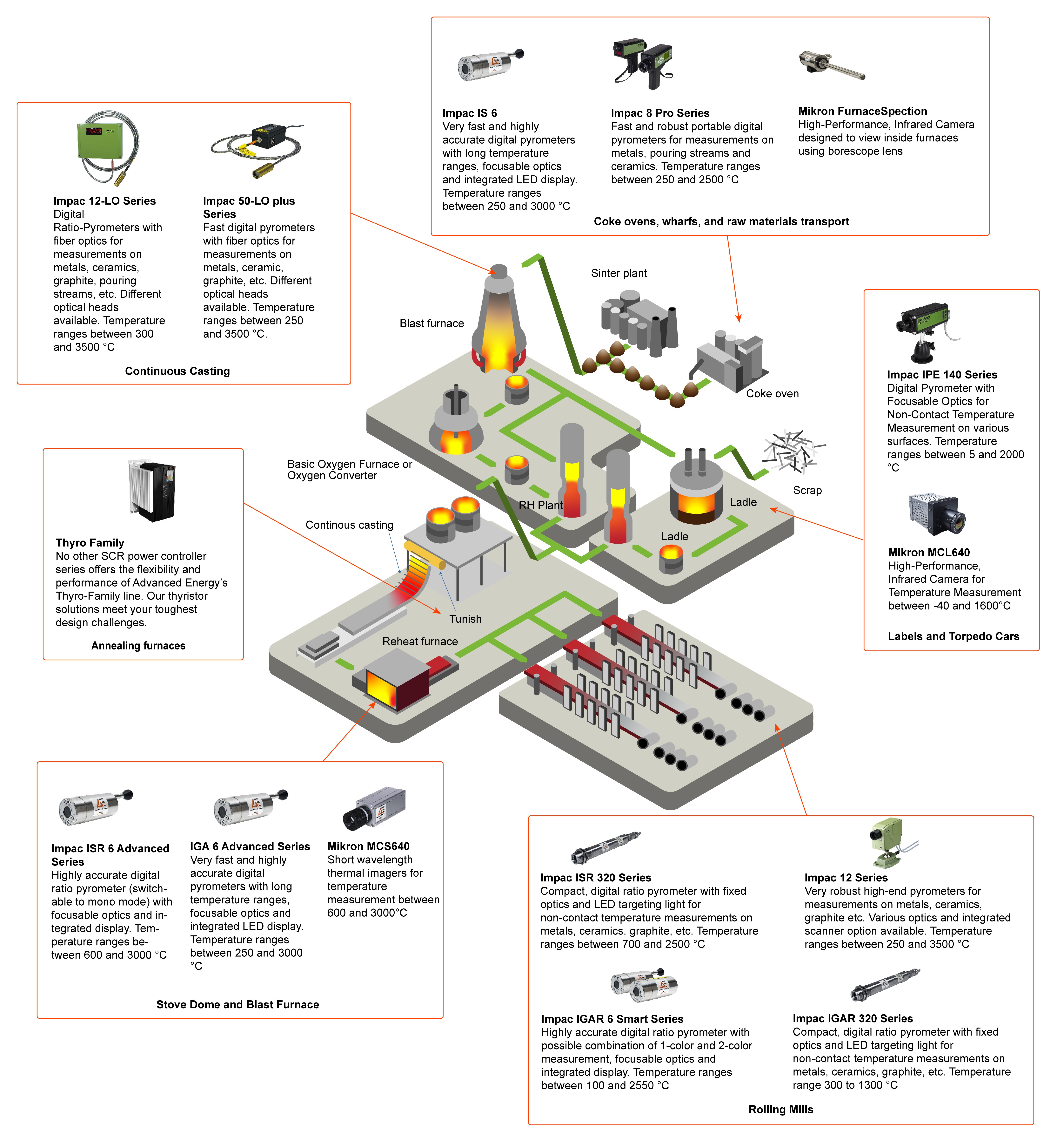
Ratio pyrometers offer significant advantages over single wavelength pyrometers in steel manufacturing applications, particularly in challenging environments. Also known as two-color pyrometers, ratio pyrometers are less affected by contaminants such as dust, steam, or smoke so they provide more accurate readings in harsh conditions. They compensate for variations in emissivity, ensuring reliable measurements even when the emissivity of the object changes. Additionally, they can measure temperatures of smaller objects better than single-wavelength pyrometers, delivering consistent temperature measurement and control, and improved process repeatability and product quality.
How do fiber optic pyrometers enable temperature measurement in continuous casting and other challenging steel processes?
Fiber optic pyrometers are crucial in continuous casting and other challenging steel processes because they can accurately measure high temperatures without being affected by ambient conditions. These pyrometers utilize optical fibers to transmit radiation between an optical head and a measuring transducer, allowing them to function effectively in high ambient temperatures and electromagnetic fields. They deliver precise monitoring of molten steel as it cools and solidifies in the continuous casting process, ensuring product uniformity and quality. By providing immediate temperature readings, they help operators control the cooling rate and process speed effectively, leading to improved slab and billet quality.
Why do SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) power controllers provide better temperature control than mechanical contactors in annealing furnaces?
SCR power controllers provide superior temperature control compared to mechanical contactors thanks to their ability to precisely modulate the amount of power delivered to the heating elements. While mechanical contactors operate in an on/off manner, SCR controllers enable continuous adjustments to the power level, ensuring consistent and stable temperature regulation. This continuous modulation helps avoid temperature fluctuations that can lead to inefficiencies and uneven heating in annealing furnaces. Additionally, their solid-state design enhances reliability and reduces maintenance needs because there are no moving parts that can wear out over time.
What temperature ranges do various steel manufacturing processes require, such as blast furnace monitoring and hot rolling?
In steel manufacturing, blast furnace monitoring involves temperatures that can reach up to 2600°C due to the presence of volatile gases used for heating along with waste gases. For hot rolling processes, temperature control is critical. Typically, hot rolling occurs at temperatures above the recrystallization point of steel, which is around 1200°C.
How do modern pyrometers compensate for emissivity variations and different infrared radiation properties of various steel alloys?
The advanced technologies of multi-wavelength pyrometers utilize application-specific algorithms to adapt to unique emissive characteristics. These techniques ensure accurate temperature measurements despite changes in material properties. Two-color (ratio) measurement provides immunity to emissivity changes and contamination. Pyrometers may also use active emissivity compensation for real-time correction of variations during processing.
What are the key considerations when selecting thermal imaging vs. spot pyrometers for steel plant monitoring applications?
Each technology offers distinct advantages, and the choice depends on factors such as the required level of detail, the environmental conditions, and the specific monitoring needs of the steel plant. When selecting between the two, it is important to consider the application’s requirements. Thermal imaging provides excellent spatial and temperature resolution for real-time monitoring and detailed image data transfer to a central PC. This is beneficial for assessing larger areas and obtaining comprehensive thermal profiles. They are suitable for environments requiring continuous operation monitoring and detailed image analysis capabilities. Spot pyrometers, especially two-color (ratio) varieties, are ideal for dirty, hot environments with steam, smoke, and dust. They can provide accurate temperature measurements unaffected by contaminants.
How do you prevent measurement errors when monitoring steel surface conditions affected by scale, oxidation, and steam?
To prevent measurement errors, specialized instruments handle varying conditions typical of industrial environments. Regular calibration and maintenance of these instruments ensure measurements remain accurate over time. Implementing standardized procedures for measurement can help reduce human error and inconsistency. Additionally, employing advanced sensor technologies, such as infrared thermography or laser scanning, can further enhance accuracy by providing non-contact measurements that are less susceptible to environmental interference. Finally, data acquisition software can analyze results in real time, allowing for immediate adjustments and verifications.
How do you ensure uniform temperature control and minimize wasted energy?
SCR power controllers offer fine control over heating rates and temperatures, reducing overshoots and minimizing wasted energy. By matching power input closely with the process requirements, these controllers enable uniform temperature distribution, which enhances process efficiency and product quality. Additionally, SCR controllers can integrate with advanced process control systems, allowing for real-time adjustments and improvements based on feedback, further optimizing energy use. Their inherent ability to quickly respond to dynamic changes in the heating process also contributes to lowering energy consumption without compromising results.
How do SCR power controllers reduce energy consumption in steel heat treatment processes?
Precise management of the electricity flow to heating elements ensures optimal energy use. SCR controllers offer fine control over the heating rates and temperatures, reducing overshoots and consequently minimizing wasted energy. By matching power input closely with the process requirements, they enable uniform temperature distribution, which enhances process efficiency and product quality. Additionally, SCR controllers can integrate with advanced process control systems, allowing for real-time adjustments and improvements based on feedback, further optimizing energy use. Their inherent ability to quickly respond to dynamic changes in the heating process also contributes to lowering energy consumption without compromising results. They minimize cycle time, enhance throughput, extend the life of equipment, and provide significant cost savings by optimizing energy use.
What role do non-contact temperature sensors play in achieving greater efficiency in steel production processes?
Non-contact temperature sensors, such as pyrometers, allow for the accurate measurement of surface temperatures without interfering with the process. They help optimize furnace temperatures, improve cooling rates, and ensure uniform heating, leading to better energy efficiency and product quality.
How does the integration of pyrometers with SCR controllers impact product quality and manufacturing efficiency in steel applications?
Integrating pyrometers with SCR controllers allows for real-time temperature feedback that adjusts the heating elements' power output. This synergy enhances temperature uniformity and process control, reducing scrap rates and improving product consistency.
.jpg)



































